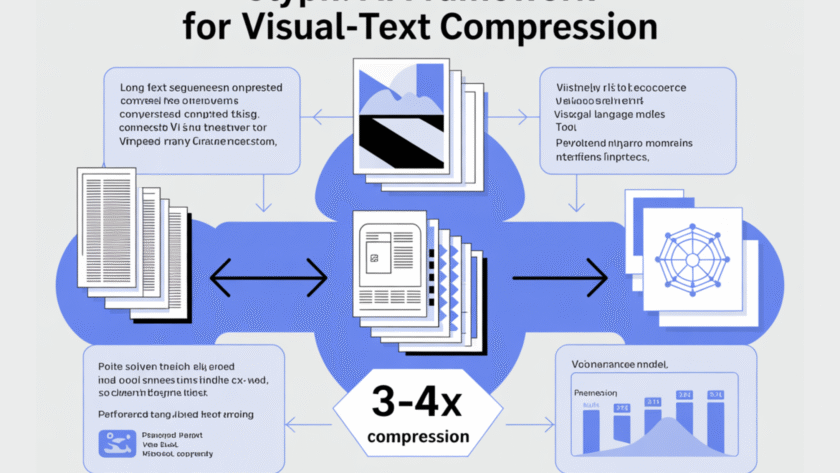
Can we render long texts as images and use a VLM to achieve 3–4× token compression, preserving accuracy while scaling a 128K context toward 1M-token workloads? A team of researchers from Zhipu AI release Glyph, an AI framework for scaling the context length through visual-text compression. It renders long textual sequences into images and processes…